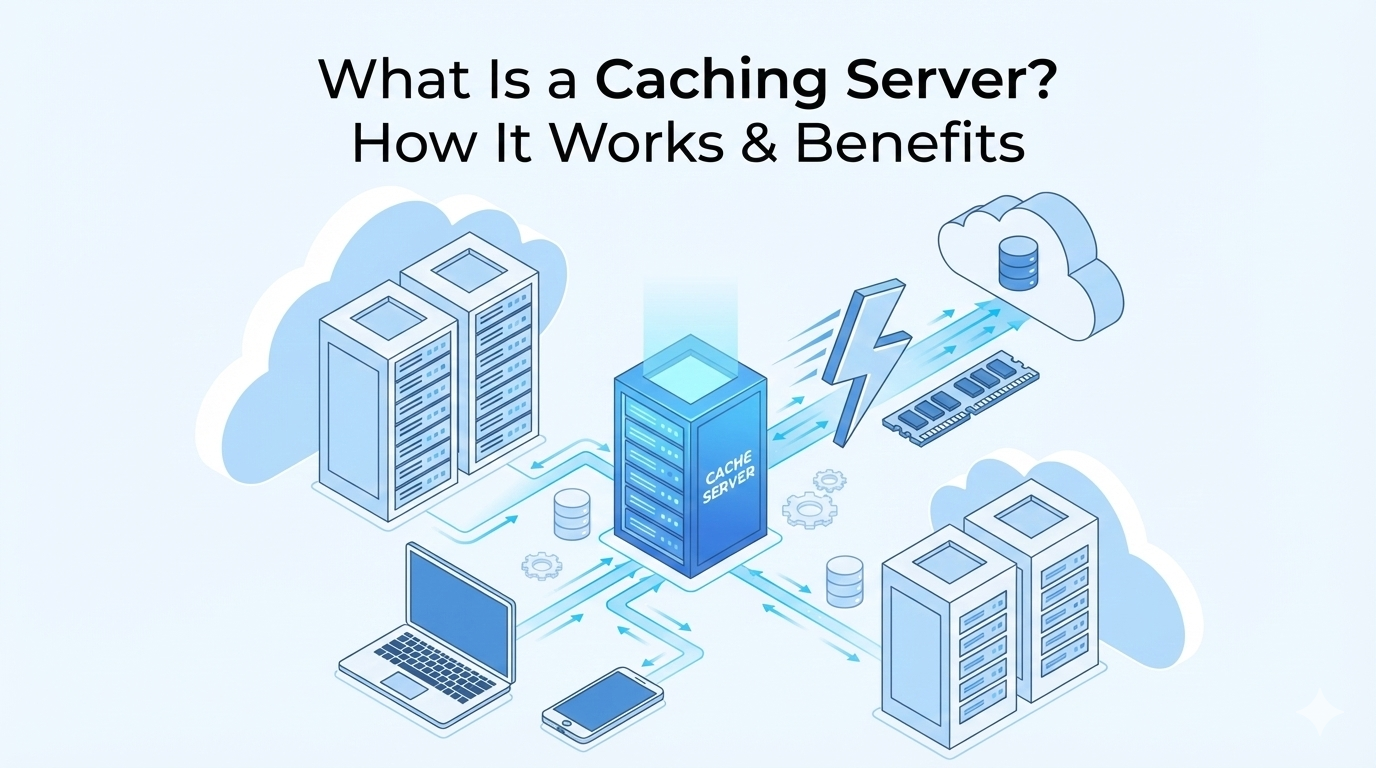
A caching server plays a significant role in offering fast, seamless, and effective web experiences. No matter if you are running a small website, an enterprise application, or a global content platform, caching servers help in decreasing server load, speeding up content delivery, and optimizing entire performance.
By temporarily gathering frequently accessed data, including images, scripts, database queries, and web pages, a caching server ensures users receive content faster without repeatedly fetching it from the origin server.
In this post, we are going to explain everything about how caching servers work, their benefits, and the types of caching. Whether you are a beginner or a pro admin, this post will cover everything you need to know about caching concepts clearly.
Cache Server: What is it?
When it comes to computing, a cache server refers to a type of network service that saves Internet content and web pages locally. It is a high-speed data storage server that keeps a subset of data so that future requests for that data are served up faster than accessing the primary storage location.
Understanding Caching
Caching is the process of storing data in a cache server. Caching improves and assists faster access to data with the objective of improving system performance. Organizations such as Google, Facebook, Amazon, and more make use of caching in their applications and services.
How does Caching server work?
Generally, data cached is stored in a fast-access hardware, such as a RAM with or without correlation with software components. Good caching trades off capacity for speed. A cache mainly stores a subset of data, unlike a database, whose data is usually complete and durable. Moreover, caching in memory is very fast because of the high request rates of input/output operations per second. Caching can be used to reduce latency.
Key Benefits of Caching
There are several advantages of caching, such as a reduction in database cost. Here are a few advantages of caching:
Overcome load on the backend server: It is achieved by decreasing the amount of data and the number of times the backend server serves continuous requests to its clients.
Application Performance: The Random Access Memory is faster than other persistent storage, like as SSDs. It improves data access speed and hence improves the entire performance of the application.
Decreased Database Cost: This is achieved by lowering the number of database instances required for your application. More database examples mean more cost. This cost is basically decreased by caching data. All in all, caching fosters your application performance by decreasing server round-trip times for fetching data from the database by persisting data in memory.
Cache Options: A good and highly performant cache server should have the following cache options.
Purge Cache: A purge cache enables you to refresh all or selected cache files. An effective caching system should take a shorter amount of time to generate through the network of servers and purge files.
Period Cache: A period cache enables you to specify the amount of time an object or data served by the cache is refreshed. This is beneficial for bulk file management.
Types of Caching
Database Caching: Excessive database queries can lower system performance as a whole. We can improve our database’s throughput and reduce the delay of data retrieval by using database caching. Any kind of database, including relational and NoSQL databases, can have a database cache layer deployed in front of it.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Caching: A content delivery network refers to a network of servers to copy your complete infrastructure across the globe. Because of the proximity of the proxy server to the user making the requests, a content delivery network offers the content requested faster.
Domain Name System (DNS) Caching: Each request made to a domain name on the Internet necessarily queries DNS cache servers to resolve the IP address associated with the domain name. DNS caching can occur on several levels, including on the OS, via ISPs, and DNS servers.
Thus, it is crucial to understand the basic principles of Caching, a caching server, and the types of caching servers. Caching is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It is vital to investigate your software desired, site visitors’ staples, and data characteristics to put in force the only caching approach.